When it comes to understanding the sources of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, it’s important to look beyond just individual actions and consider the role that different sectors play. From housing and transportation to industry and agriculture, various industries and activities contribute to the release of CO2 into the atmosphere. In this article, we’ll take a comprehensive look at the shares of each sector on CO2 emissions, including the impact of housing, military, wars, cruise ships, cars, industry, farming, buildings, and electricity.
Housing and Transportation: Major Contributors to CO2 Emissions
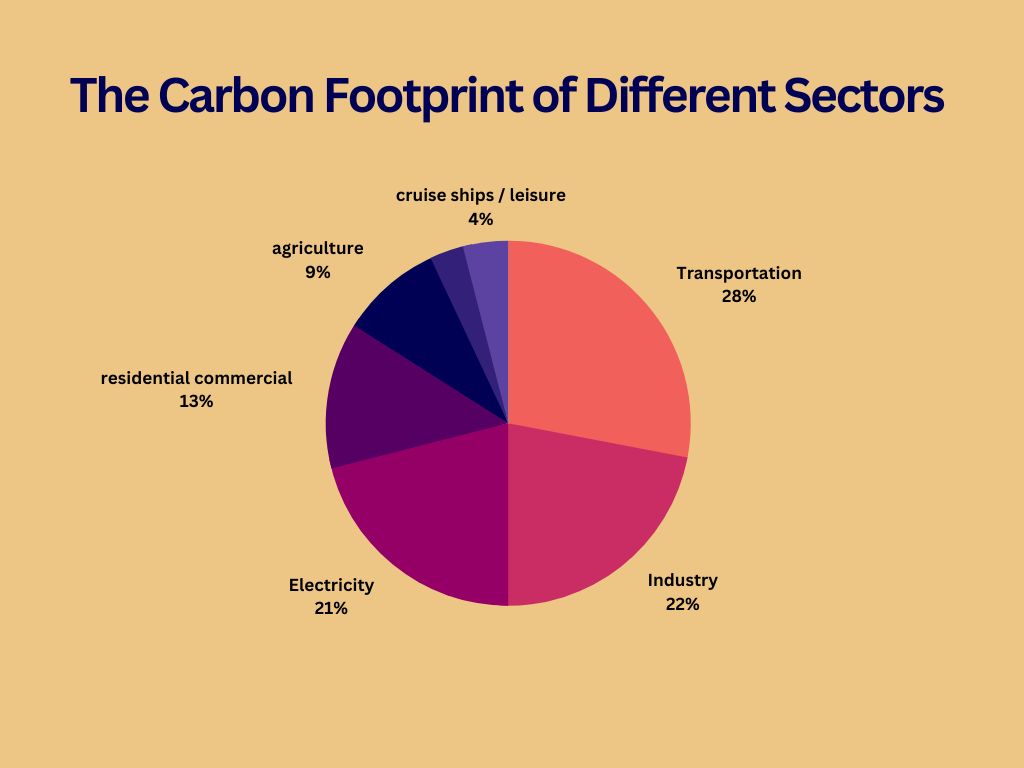
One of the largest sources of CO2 emissions is the transportation sector, which includes everything from cars and trucks to planes and trains. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), transportation accounted for 28% of total U.S. CO2 emissions in 2019. The majority of these emissions come from gasoline- and diesel-powered vehicles, which release CO2 as a byproduct of burning fossil fuels.
Housing is another major contributor to CO2 emissions. Heating, cooling, and powering homes and buildings requires a significant amount of energy, much of which is generated using fossil fuels such as coal and natural gas. In the U.S., the residential and commercial sectors combined accounted for about 12% of total CO2 emissions in 2019, according to the EPA.
Industry, Electricity, and Agriculture: Not Far Behind
Industry is another major source of CO2 emissions, accounting for about 22% of total emissions in the U.S. in 2019. This includes emissions from manufacturing, construction, and other industrial activities. The use of fossil fuels for energy, as well as the release of CO2 from chemical reactions during manufacturing processes, contribute to these emissions.
Electricity generation is also a significant source of CO2 emissions. In the U.S., electricity accounted for about 21% of total CO2 emissions in 2019. Most of this electricity is generated using fossil fuels, which release CO2 when burned. The use of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, can help reduce these emissions.
Agriculture is another sector that contributes to CO2 emissions, although to a lesser extent than some of the others. The EPA estimates that agriculture accounted for about 9% of total U.S. CO2 emissions in 2019. Emissions from agriculture come from a variety of sources, including the use of fossil fuels for machinery and transportation, as well as the release of CO2 from livestock and the decomposition of organic matter.
Military and Wars: A Significant but Often Overlooked Source of CO2
The military is a significant contributor to CO2 emissions, although it is often overlooked in discussions about the environment. Military activities, including training exercises and wars, require the use of fossil fuels for transportation and energy, which releases CO2 into the atmosphere
Summary
- Transportation: 28%
- Industry: 22%
- Electricity: 21%
- Housing (residential and commercial): 12%
- Agriculture: 9%
- Military and wars: 3%
- Cruise ships and other leisure activities: 4%
Keep in mind that these percentages may vary slightly depending on the source and the specific calculations used. This list is intended to give a quick overview of the relative contributions of each sector to CO2 emissions. Find more details on our world in data

Leave a Reply